Background
Glioblastoma is a highly aggressive form of primary brain tumor that is not fully understood. Even with our current advancements in treatments, the survival rate of patients is very poor. Therefore, research is being done in detecting and understanding Low-Grade Glioblastoma in hopes of providing better treatment.
Objectives
Goal of the Capstone:
- Create a process to create biologically relevent models using Pathway Analysis.
- Use these different models to detect Low-Grade Glioblastoma.
- Explore casuality between pathways using a Bayesian Network.
- Compare the Pathway created models to Gene created models.
Dataset
The dataset used for this capstone was the REMBRANT dataset. This dataset consisted of genetic expression data for patients that had Glioblastoma.
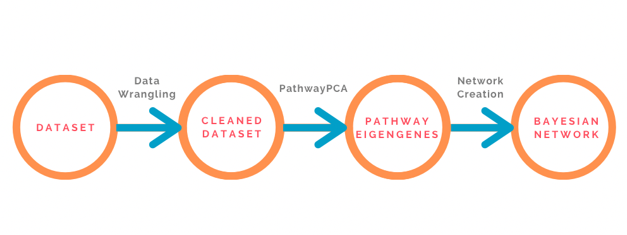
Methods
To achieve the goals laid out, a process was created in which Pathway Eigengenes were used to give biological direction to the models. These Pathway Eigengenes were created using a package called PathwayPCA. The Pathway Eigengenes were then used to create Bayesian Networks and other classification models that could be used to predict Low-Grade Glioblastoma. In addition, the Bayesian Networks were explored and analyzed for biological significance and relevance.
Classification Results
Accuracy results show that the Pathway Approach gave an increase in accuracy for most models.
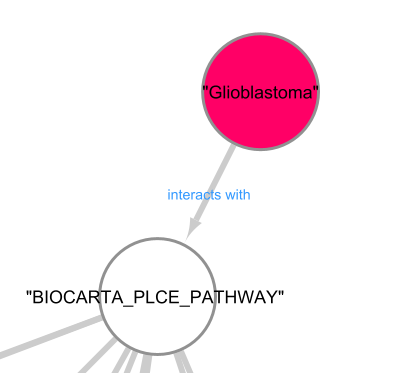
Literature Analysis
Pathway Node directly connected to the Glioblastoma Node in the Pathway Approach Bayesian Network.
Gene Nodes directly connected to the Glioblastoma Node in the Gene Bayesian Network.
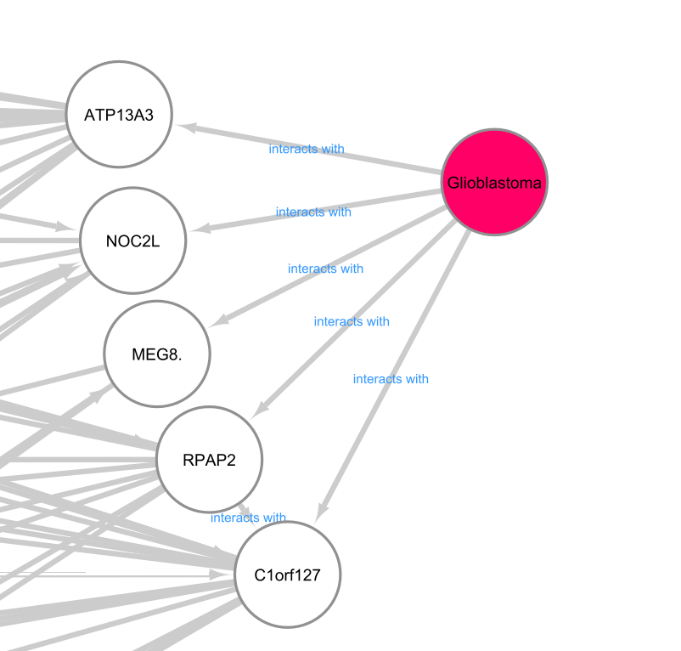
While the Gene network made more connections, literature analysis showed that not all genes were biogically relevant. This shows the advantages of using a Pathway Approach when working with biological data.
Conclusion
The Pathway Approach created models that were biologically relevant and more accurate than models created using Genes. In addition, the Bayesian Network approach proved to be advantageous because it can be used to delineate pathways that are associated with Glioblastoma, unlike the other algorithms that function more as a classifier. If combined with new research, this approach could be used to help Clinicans detect Glioblastoma earlier and better coordinate treatment in hopes of raising the survival rate of patients.